Did you know that egg quality declines significantly after the age of 35, but embryo quality isn’t solely dependent on egg health? While both egg and embryo quality play crucial roles in the success of IVF, understanding which one has a greater impact is essential for couples seeking fertility treatment. This blog aims to compare the importance of egg quality and embryo quality in IVF success and help you determine which factor is more crucial for successful implantation and pregnancy.
1. What Is Egg Quality?
Egg quality refers to how well an egg can mature, fertilise, and develop into a viable embryo. Healthy eggs have the potential to produce high-quality embryos that are more likely to result in successful pregnancies.
Factors Affecting Egg Quality:
- Age: As women age, especially after 35, the quantity and quality of their eggs decline, leading to a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Lifestyle: Diet, smoking, alcohol consumption, and stress can all impact egg health.
- Genetics and Medical Conditions: Certain genetic conditions and underlying medical issues (like PCOS or endometriosis) may affect egg quality.
Why It Matters:
Poor-quality eggs may fail to fertilise, lead to chromosomal abnormalities, or result in poor-quality embryos, which decreases IVF success rates.
2. What Is Embryo Quality?
Embryo quality refers to the potential of a fertilised egg (embryo) to implant and develop into a healthy pregnancy. An embryo’s ability to divide and grow properly after fertilisation is key to achieving successful implantation.
- Factors Affecting Embryo Quality:
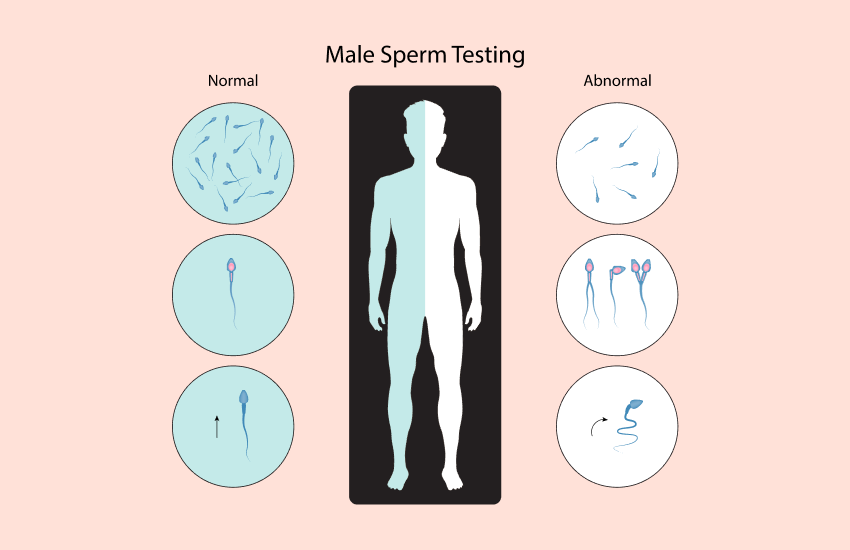
- Egg and Sperm Quality: Both the egg and sperm contribute to embryo health.
- Lab Culture Conditions: The environment in the laboratory during embryo culture plays a significant role in embryo development.
- Genetic Integrity: Genetic screening, such as Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), ensures the embryos are free from chromosomal abnormalities.
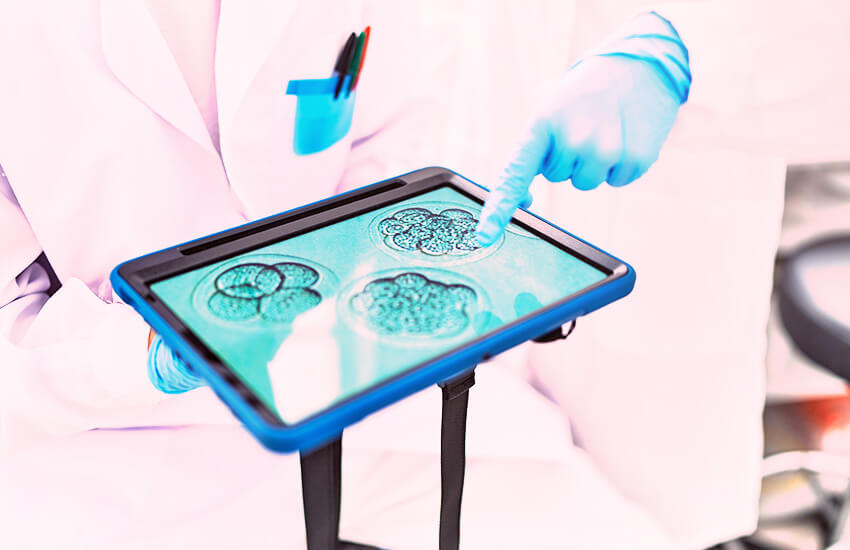
- How Embryos Are Graded: Embryos are graded based on their appearance and developmental stages. Common grading systems include:
- Day 3 Embryos: Graded based on cell count and symmetry.
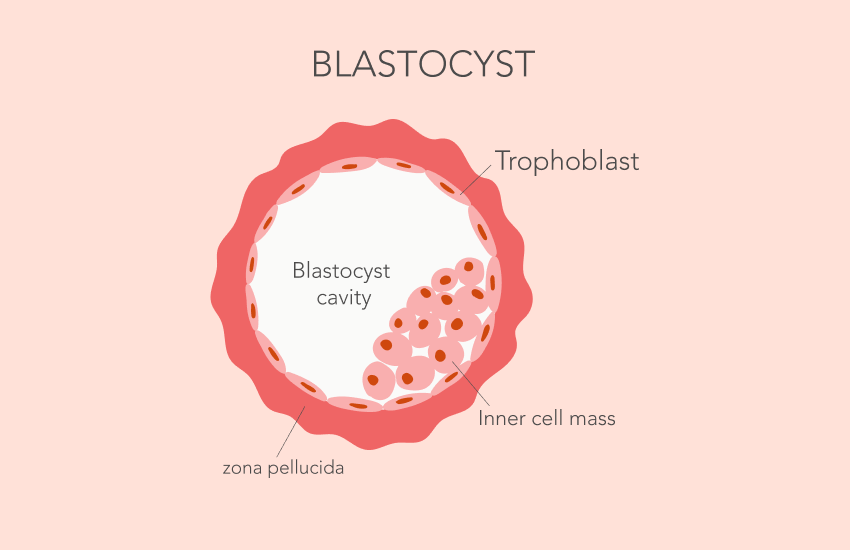
- Day 5 Blastocysts: More advanced, with grading based on the blastocyst’s expansion and inner cell mass.
Egg Quality vs. Embryo Quality: Which Matters More?
While egg quality is the foundation of a successful IVF process, embryo quality is critical for successful implantation and achieving a healthy pregnancy. The two are interconnected, and their importance cannot be separated. Egg quality affects the initial fertilisation process, and poor-quality eggs can result in poor-quality embryos, leading to a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities and implantation failure.
On the other hand, embryo quality plays a crucial role in the implantation phase. Even if the egg quality is good, the embryo’s ability to develop and attach to the uterine lining is vital for a successful pregnancy. Both egg and embryo quality are equally important in the IVF process, and optimal egg health can increase the likelihood of producing high-quality embryos.
Improving Egg and Embryo Quality for IVF
To optimise your chances of a successful IVF outcome, improving both egg and embryo quality is essential. While many factors are beyond our control, there are several lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and advanced techniques that can help enhance both aspects, increasing the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
Final Thoughts
Both egg and embryo quality are crucial factors for IVF success. While egg health plays an essential role in creating good-quality embryos, embryo quality is what ultimately determines whether implantation and pregnancy occur. Patients undergoing IVF should focus on improving overall reproductive health and discuss embryo grading with their fertility specialist to maximise their chances of success.
Get the Best IVF Outcomes with Dr Deepali Chinchole’s Expertise
Struggling with IVF success? Consult with Dr Deepali Chinchole, a leading fertility doctor in Pune at FYNE IVF, to optimise both egg and embryo quality for the best outcomes. With her expertise in assisted reproductive technologies, she will guide you through the process of enhancing your chances of successful implantation and pregnancy. Schedule your consultation today and take the next step toward fulfilling your parenthood dreams!
FAQs
What is considered a good-quality egg for IVF?
A good-quality egg has a normal appearance, with a clear shape and healthy chromosomes, making it more likely to fertilise and create a viable embryo.
Can a poor-quality egg still result in a successful pregnancy?
While it’s more challenging, poor-quality eggs may still result in a healthy pregnancy, but the risk of miscarriage or chromosomal abnormalities increases.
How can I naturally improve egg quality?
Eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, exercising regularly, and taking supplements like CoQ10 and folic acid may help improve egg quality naturally.
What are the grading criteria for high-quality embryos?
Embryos are graded based on cell structure, symmetry, and their ability to reach the blastocyst stage. Day 5 blastocysts typically have higher implantation potential.
Does embryo freezing affect its quality?
While the freezing and thawing process can have minor impacts on embryo quality, embryo freezing is generally considered safe and allows for the preservation of high-quality embryos for future use.